About Goldman Sachs 2025
APPLICATION DETAILS : Registrations for the program start from March 7 , 2025. Last date to apply is March 23 , 2025.
ELIGIBLITY : Final year students; Graduating in 2025; Date of Joining: July 2025
LOCATION : Bengaluru, Hyderabad
Goldman Sachs Recruitment Process , Exam Pattern 2025
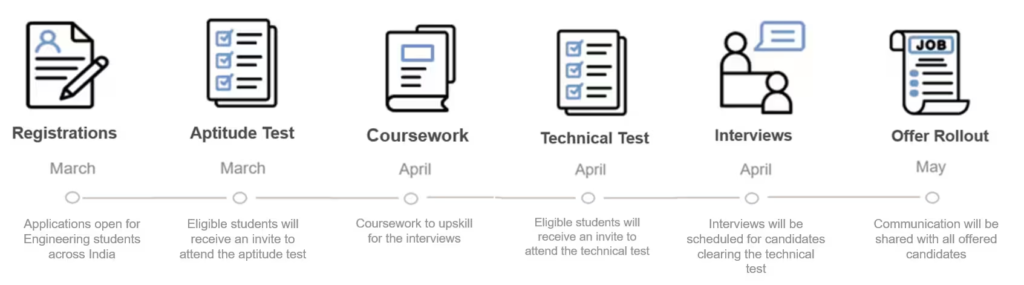
Goldman Sachs Updated Syllabus 2025
Goldman Sachs Aptitude Questions
Numeric COMPUTATION (12 QUESTIONS)
1.Linear Algebra: Matrix operations, eigenvalues, eigenvectors, and applications.
2.Numerical Integration and Differentiation: Approximation techniques like Simpson’s Rule or Gaussian Quadrature.
3.Optimization: Finding minima or maxima using methods like gradient descent or simplex algorithms.
4.Solving Systems of Equations: Iterative and direct approaches like Gaussian Elimination and Jacobi Method.
NUMERIC REASONING (12)
1.Arithmetic Calculations: Operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, including decimals and fractions.
2.Number Sequences: Recognizing patterns and predicting the next numbers in sequences.
3.Ratios and Proportions: Solving problems involving comparisons and relationships between numbers.
4.Percentages: Calculating increases, decreases, and proportions in percentage terms.
5.Basic Algebra: Simplifying expressions and solving equations.
6.Graphs and Tables: Reading and interpreting data presented visually.
7.Data Analysis: Summarizing data using mean, median, mode, and range.
8.Probability and Statistics: Assessing likelihoods and analyzing datasets.
ABSTRACT REASONING (12)
1.Pattern Recognition: Identifying sequences or trends in shapes, symbols, or numbers.
2.Spatial Reasoning: Visualizing objects in space, rotations, and transformations.
3.Analogies: Understanding relationships between pairs of items or concepts.
4.Deductive Reasoning: Drawing specific conclusions based on general principles or rules.
5.Inductive Reasoning: Making generalizations from specific examples or observations.
6.Problem Solving: Using logic to navigate through complex situations or puzzles.
7.Critical Thinking: Analyzing and evaluating ideas to form judgments or solve problems.
8.Symbolic Logic: Understanding logical operations involving symbols and their relationships.
9.Series and Sequencing: Determining what comes next in a sequence of shapes, colors, or figures.
Diagramatic Reasoning
1.Shape Sequences: Identifying the next shape or figure in a series based on a pattern.
2.Mirror and Rotational Symmetry: Analyzing how shapes transform with reflections or rotations.
3.Analogies in Diagrams: Understanding relationships between pairs of figures or diagrams.
4.Matrices with Patterns: Completing matrices by determining relationships between visual elements.
5.Flowcharts and Processes: Interpreting and reasoning through process diagrams or flowcharts.
6.Visual Grouping: Classifying shapes or figures based on shared properties.
7.Odd-One-Out Problems: Identifying the diagram that doesn’t fit with the rest.
8.Spatial Orientation: Understanding how objects are arranged in space, such as folding or stacking.
9.Transformations: Solving problems involving translations, scaling, or deformation of shapes.
10.Proportions and Ratios in Visuals: Using visual data to determine numeric or spatial relationships.
LOGICAL REASONING (12)
1.Deductive Reasoning: Drawing conclusions based on general principles or premises (e.g., syllogisms, conditional reasoning).
2.Inductive Reasoning: Forming generalizations from specific observations or examples.
3.Analytical Reasoning: Solving puzzles or problems involving relationships between elements (e.g., seating arrangements, grouping tasks).
4.Critical Thinking: Evaluating the strength and validity of arguments, identifying assumptions and biases.
5.Cause and Effect: Analyzing relationships between actions and outcomes.
6.Sequences and Series: Identifying logical patterns in numbers, letters, or events.
7.Analogies: Comparing relationships between pairs of concepts, ideas, or objects.
8.Statements and Assumptions: Evaluating whether conclusions logically follow from given statements.
Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension is the ability to understand, interpret, and analyze written texts. It goes beyond simply reading words—it involves grasping the meaning, context, and deeper nuances of the content. Here are some elements involved in reading comprehension:
- Decoding: Recognizing words and understanding their meaning.
- Understanding Vocabulary: Building a strong vocabulary to make sense of unfamiliar terms.
- Contextual Interpretation: Relating the text to its context or background.
- Main Idea Identification: Determining the central theme or message of the text.
- Inference: Drawing conclusions or reading between the lines based on the given information.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluating arguments, perspectives, or ideas presented in the text.
- Retention: Remembering key points and details for future reference.
About KN Academy
Welcome to KN Academy Jobs, the premier online job portal for off campus job opportunities. Our mission is to connect talented job seekers with top employers and help them find the perfect fit for their career goals.
We Provide Recent OFF Campus Hiring Drives For 2020/2021/2022/2023 Batch Students. The Domain in Which We Cover Hirings Are Software Engineering , Data Analysis , Web Development
Our Channel Post Jobs For Freshers / Experienced People With Full Job Description Including Hiring Batch , Experience Required
Qualification.
One of the main advantages of fresher jobs is that they provide a platform for individuals to gain valuable work experience, develop new skills, and build a professional network. Many organizations offer on-the-job training and mentoring programs, which can help freshers to quickly adapt to the work environment and advance in their careers.
However, finding a fresher job can be challenging, as there is a lot of competition for entry-level positions. It’s important for freshers to be proactive and take a strategic approach to their job search.
Join Telegram – click here to join
